Resonant Slot Antenna
FIELD: radio engineering, communication.

- The height of the hexagonal slot H, which can be varied to achieve the different resonant frequency. With this variation, the overall length of the stub also varies which in turn enables the antenna to resonateat different frequency. 3 shows the return loss plot of the antenna when H=17, 18, 19 and 20.
- An optimized low-profile antenna that consists of a rectangular resonant cavity and nonuniform radiation slots is presented. The antenna has a pencil-beam radiation pattern, low sidelobes, and can.
SUBSTANCE: waveguide line, on one wall of which there are radiating elements and at the end of which there is a tuning element, includes phase-shifting devices mounted between radiating elements and between a radiating element and the tuning element, and communication elements connected to the waveguide, wherein the phase-shifting devices change the phase of the transmitted microwave signal in a wide range depending on its power level.

EFFECT: wide operating frequency range without deterioration of the directivity index and matching the antenna while maintaining the direction of the main directional lobe, as well as low cost and high technological effectiveness.
1 dwg
One slot is formed at the bottom side of this cavity as a feeding slot to excite two orthogonal resonant modes. The slot antenna is then constituted at the opposite side of the feeding slot to radiate electromagnetic wave.
The invention relates to antenna technique and can be used to create antenna systems in the radionavigation and radiolocation.
When creating various radio navigation (radar) devices, the challenge is to create an antenna operating in two different bands, such as antenna systems, secondary radar, designed for air traffic control, and in the same range is transmitted signal and the other receiving. The antenna must have a small weight, low cost and high manufacturability and to withstand high mechanical loads. These properties have a resonant waveguide-slot antenna, which is made on the basis of the waveguides, resonators, or strip line. (Antennas and microwave device. Vasyliev, Lionaires, Austine. Edited by Prof. Digestmessage. M, Chapman and hall, 1994.).
So, in a remote analogue of the claimed invention - resonant waveguide-slot antenna containing a rectangular waveguide, in one of the walls is made of radiating slits, and short-circuited the piston is located at the end of the antenna, and the distance between the slits multiple of half the wavelength in the waveguide. (The VHF antenna. Yea, Vghemasti, Antiricin. H 2. M, Communication, 1977.) provides light weight, low cost, high performance.
Od is ako the antenna inherent drawback: since each slit separately not consistent with the waveguide, all reflections from cracks waves are combined at the antenna input reflection coefficient of the system becomes large. This misalignment can be compensated at the antenna input using the setting item (usually the short-circuit piston), but at low frequency coordination is impaired and, therefore, the antenna will remain narrow. (Antennas and microwave device. Vasyliev, Lionaires, Austine. Edited by Prof. Digestmessage. M, Chapman and hall, 1994.). Moreover, when changing frequency changing not only the coordination of the antenna, but also other parameters. At frequencies other than resonance, the distance between the emitters is not equal to half of the wavelength and therefore the gap in the antenna excited unevenly and desipate, which leads to a distortion of the directional diagrams. The expansion band is possible by reducing the number of slits (the VHF Antenna. Yea, Vghemasti, Antiricin. H 2. M, Communication, 1977.), but this inevitably leads to an increase in width of the main lobe of the radiation pattern, which is highly undesirable. Wide pattern does not allow for high resolution angular coordinates, and to ensure the required service area increases the width of the main lobe of the directivity diagram leads to the necessity of increasing the radiated power before which tcheka, increase the sensitivity of the receiving equipment. All this leads to considerable complication of the entire product and increase its value. In addition, it is impossible to ensure coordination in the case, if the antenna is designed to work in two rather widely separated frequency ranges.
The closest analog is selected as the prototype due to the similarity performed technical tasks, is a waveguide-slot antenna (awts of the USSR №1171887, H01Q 13/10,1985), containing a rectangular waveguide, one wall of which is made emitting slit, the causative agent of fashion Hoi, absorptive load, volumetric resonator mounted on the outside of the rectangular waveguide and coupled with it the communication hole, the semiconductor switch installed inside a rectangular waveguide between the dummy load and the last of the radiating slot at a distance from it equal to a quarter wavelength in a rectangular waveguide, corresponding to the position of the beam normal to the axis of the antenna, the detector is placed in a three-dimensional resonator, and the amplifier-limiter, and the detector, the amplifier-limiter and the semiconductor switch are connected in series.
This antenna has more channels, since the antenna is consistent not only on the frequency corresponding to the beam position on armali to the axis of the antenna, but at other frequencies, however, when changing the frequency changes the direction of the main lobe of the radiation pattern. This makes it impossible to use this antenna for the decision of tasks to ensure system operability secondary radar. Secondary radar to ensure their health needs to the antenna at different frequencies, at least, had the same direction of the main lobe of the radiation pattern.
The technical result of the invention is the extension of the operating frequency range without deterioration factor directional and coordination of the antenna while maintaining the direction of the main lobe of the pattern, as well as low cost and high technology.
This technical result is achieved that the surge line on one of the walls which are emitting elements, and at the end of the setting item entered phase-shifting devices installed between the radiating elements and between the radiating element and the adjustment element, and the phase-shifting device widely change the passing phase of the microwave signal depending on the level of his power.
The known device using the difference between the power levels of the incoming microwave signals (I.V. Lebedev, who Sitnikov A.S., Merchants H. Solid-state microwave limiters problems and solutions (overview). WPI. universities MB and MDA of the USSR. Electronics, 1985, V.28, No. 10). However, these devices serve or protect receivers from strong signal (microwave limiters)or accession (toggle) input device to one of its outputs (for example, switches transfer), i.e. have a different technical problem.
The known device, changing in a wide range passing phase of the microwave signal (SHF phasers and switches. Features create a p-i-n diodes in integrated circuits. Hut G.S., Vendik IB, Serebryakova E.A.), Radio and communication, 1984). However, in all known phase-shifting devices, the phase change is not due to the difference in levels of passing power, and by supplying an external control low-frequency signal and does not depend on the level of passing power. Using an external low-frequency control signals to produce the necessary phase shift held UHF signal leads to an increase in weight and performance, increase energy, reduce reliability, poor processability, increase the cost of the antenna.
Therefore, discusses the design characteristics of these devices or used it for any other purpose or lead to an increase of massagana etnich indicators the increase in energy consumption, reduction of reliability, that is unable to provide work waveguide-slot-resonant antenna at two different frequencies while maintaining low cost and high processability of the antenna.
This allows to make a conclusion on the compliance of the claimed invention with the patentability criterion of 'inventive step'.
Figure 1 shows the proposed waveguide-slot antenna.
Waveguide-slot antenna includes a waveguide line 1, in one of the walls which are emitting elements 2, at the end of the waveguide line is setting item 3 (short-circuited the piston) and the phase-shifting device 4 mounted between the radiating elements 2, and the phase-shifting device 5 between the radiating element 2 and the adjustment element 3 (short-circuit piston)and the associated waveguide 1 elements of communication 6.
Resonant Slot Antenna Tuner
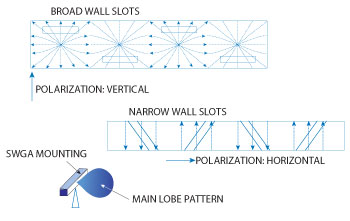
Waveguide-slot antenna operates as follows. For definiteness, consider the work of the waveguide-slot antenna with longitudinal slits (emitting elements 2)located on one side of the middle line of the broad wall of the waveguide 1. The phase-shifting devices 4, 5 can be performed in various ways, for example, according to the scheme of passing Slavnov phase shifter for microwave diodes. (Microwave phasers and switches. CCA is items created on the p-i-n diodes in integrated circuits. Hut G.S., Vendik IB, Serebryakova E. - M., 'Radio and communications, 1984, s). A characteristic feature of the proposed phase shifter from phasers, described in 'microwave phasers and switches. Features create a p-i-n diodes in integrated circuits. Hut G.S., Vendik IB, Serebryakova E.A.), Radio and communication, 1984., is the lack of control circuits and the mandatory use as switching elements limiting diodes (type AA and others) instead of switching diodes (type AA and others). This type of phase-shifting devices 4, 5 can be connected to the waveguide 1 by the connection elements 6, made for example in the form of a probe transitions. (The design of the lens, scanning, wide-band antennas and feeder devices. Beetle MS and Molochkov SHE Meters, Energy, 1973, S. 406).
Consider the transfer mode. In transmit mode, the antenna receives the signal of a large power of a certain frequency. When a signal of high power (transmission mode) of the diodes in the phase-shifting devices 4, 5, associated with the waveguide 1 by the connection elements 6, by applying a strong RF signal (without applying an external control signal) is opened. The phase-shifting device 4 (passing Slavny Phaser) with open diodes provides for the transmission frequency when the distance between the radiating elements 2 phases, the first shift is 360°. When the phase shift between the radiating elements 2, is equal to 360°emitting elements 2 (slit) are excited in phase, which corresponds to the direction of maximum radiation normal to the antenna axis. The phase-shifting device 5 installed between the last radiating element 2 and the adjustment element 3, gives the phase shift required to compensate for the mismatch at the antenna input. The direction of the main lobe of the pattern transfer mode is normal to the axis of the antenna.
Consider the receive mode. In the receive mode, the antenna receives the signal of low power with a frequency different from the frequency of the signal in the transmission mode. When a signal of low power (receive mode) diodes in the phase-shifting devices 4 are closed. Pass Slavny Phaser closed diodes provides the phase shift that the reception frequency different from the transmission frequency and at a given distance between the radiating elements 2 phase difference signal, these elements are also equal to 360°. When the phase shift between the radiating elements 2, is equal to 360°, RF signals from radiating elements 2 (cracks) as well as in the transmission mode, are in-phase. When the direction of the main lobe of the directivity diagram in receive mode is also normal to the axis of the antenna.
The phase-shifting device 5 installed between the last) is emitting element 2 and the adjustment element 3, gives the phase shift required to compensate for the mismatch at the antenna input.
Selecting the phase shifts, which gives the phase-shifting device 5 in both modes (transmit and receive), you can compensate for the mismatch at the input of the antenna in the transmit mode and the receive mode. Thus there is an additional degree of adjustment due to selection changes phase in this phase-shifting device 5.
Thus, the proposed waveguide-slot antenna operates in two different frequency ranges without compromising coordination and coefficient directional, the direction of the main beamwidths in both modes equally (normal to the axis of the antenna), and also has low cost and high technology primarily because there are no external low-frequency control signals to produce the necessary phase shift to the passing of the microwave signal, the necessity of which leads to increase in weight and performance, increase energy, reduce reliability, poor processability, increase the cost of antenna
Waveguide-slot antenna with radiating elements 2, for example made in the form of longitudinal slots located on either side of the middle line of the broad wall of the waveguide 1, p is pepper cracks and other works similarly. In addition, in the waveguide-slot antenna is often used reactive vibrators to obtain the longitudinal component of the field. Rocket vibrator is a metal rod that is screwed into the waveguide (the VHF Antenna. Yea, Vghemasti, Antiricin. H 2. M, Communication, 1977.). In this case, the possible additional use of the rod as the connection elements 6 for phase-shifting devices 4, 5, while retaining the possibility of individual adjustment of each radiating element 3.
The phase-shifting device 4 can be made not only according to the scheme of passing Slavnov Phaser, but other schemes (Antennas and microwave device. Dmessano. M., High school, 1988.).
An additional positive result of this technical solution is that the distance between the radiating elements 3 may not be a multiple of half the wavelength in the waveguide. This allows you to create an antenna with certain parameters (level near or far side lobes etc)
You can also create a waveguide-slot antenna not only in rectangular waveguide, but also on other transmission lines, such as the strip. (Antennas and microwave device. Vasyliev, Lionaires, Austine. Edited by Prof. Digestmessage. M, Chapman and hall, 1994.).
Use the top the invention allows to create a waveguide-slot antenna with a wide range of frequencies without compromising coordination while maintaining low cost and high technology.
Waveguide-slot antenna, waveguide containing a line on one of the walls which are emitting elements, the element settings that are at the end of the waveguide line, characterized in that the introduced phase-shifting device, set in between the radiating elements and phase-shifting device installed between the radiating element and the adjustment element, and associated with the waveguide elements of communication, and the phase-shifting device widely change the passing phase of the microwave signal depending on the level of his power.
FIELD: radio engineering, communication.
SUBSTANCE: circular polarisation slit stripline leaky-wave antenna includes a dielectric substrate, on the lower metal-coated side of which there is a spiral-shaped microstrip feed line, and on the top metal-coated side of which there are main slit radiators twisted on a spiral around the geometric centre of the antenna and having straight and curved segments of different length; on the top metal-coated side of the dielectric substrate between the main slit radiators there are additional slits with a shorter electrical length than that of the main slit radiators; the additional slits are not connected to the main slit radiators and are in form of concentric arcs arranged around the geometric centre of the antenna or in form of spiral sections.
EFFECT: improved technical characteristics of the antenna, specifically: low elliptic coefficient, improved suppression of cross-polarisation and wider operating frequency range.
2 cl, 11 dwg
FIELD: radio engineering.
SUBSTANCE: printed-circuit board (50) with control diagram is inserted at least in one spline of contour plate in the device containing contour plate (20) of antenna with multiple antenna splines (30, 31, 32) and at least with one control circuit (40) for excitation of antenna contour plate.
EFFECT: enlarging functional capabilities and improving compactness.
15 cl, 4 dwg
FIELD: radio engineering.
SUBSTANCE: planar antenna contains printed symmetrical slot line formed with two identical metal plates which are connected to each other with bonding strip on one side and arranged on one surface of insulating substrate on the other surface of which there located is a piece of signal strip line. Antenna aperture is formed with a piece of divergent printed symmetrical slot line, which is a continued part of the piece of printed homogeneous symmetrical slot line of conductor.
EFFECT: designing broadband antenna capable of simultaneous equal radiation and reception of longitudinal electromagnetic waves and transverse electromagnetic waves with one aperture via separate channels loosened between each other, with low nonuniformity level of matching characteristic, with simple and high-technology construction.
37 cl, 42 dwg
FIELD: physics; radio.
SUBSTANCE: invention relates to radio engineering, particularly to slotted waveguide antennae, and can be used independently or as a component of a phase antenna array (PAA) with mechanical scanning in two planes or electronic scanning in the E-plane and mechanical scanning in the H-plane. The device consists of a length of waveguide with longitudinal slots made on its wide wall and lying on different sides of axial line. The technical result is achieved due to that, the length of the rectangular waveguide has a flat-topped section with dimensions forming the outer contour on the wide wall a1=(0.45±0.05)λ0 and on the narrow wall b1=(0.26±0.05)λ0 and forming the inner contour with dimensions of the wide wall a2=(0.27±0.05)λ0 and the narrow wall b2=(0.15±0.05)λ0, where λ0 is wavelength in free space. On the wide wall there are metallic edges with radiating slots, where the edges are a continuation of the narrow walls of the outer contour with height equal to λ0/2 or greater, and the length of the radiating slots is greater than λ0/2. Dimensions and displacement relative the axis of the flat-topped waveguide are selected based on the required level of the signal radiated from each slot, and comply with the condition for minimal change of the level of signal radiated from each slot in the given frequency range.
EFFECT: reduced size of the waveguide in the E plane.
2 dwg
FIELD: radio engineering.
SUBSTANCE: proposed flat cavity antenna, which includes a first low cavity resonator with a partially transparent wall and a second resonant cavity with communication holes, which differs in that the second resonant cavity, is installed inside the first resonant cavity. The first resonant cavity contains the first plate, the first and second volumetric cells, and the second plate, made with emitting holes. The second resonant cavity is made in the form of a coaxial resonator with open ends; slots are made on the outer conductor of the coaxial resonator, the outer and inner coaxial conductors are connected together with a short-circuiting switch. The second resonator is connected with the feeder line.
EFFECT: small sizes of antennas, good antenna matching with the feeder line, low level of lateral and rear emission, low level of cross polarisation emission, high efficiency of the antennas, low losses of electromagnetic energy in the feeder line, low antenna noise temperature, high level of electromagnetic compatibility, aesthetic look.
11 cl, 9 dwg
FIELD: medicine.
SUBSTANCE: emitter of superhigh frequency electromagnetic waves for hyperthermia includes the quarter-wave resonator based on non-symmetrical microstrip transmission line, which consists of dielectric base, screen conductor, emitting conductor and input coaxial plug. The input coaxial plug is installed outside the thermo emission zone of electromagnetic emission from the emitting conductor and radiation field of the source of γ-irradiation, and plugged to the emitting conductor and screen conductor of the microstrip transmission line via L-shaped filter, which includes the strip powering line in power point of the quarter-wave resonator and container.
EFFECT: efficiency of radiation effect on tumor is increased.
2 dwg, 1 tbl
FIELD: printing antennas with double polarization with power from commutation field located on electronic board.
SUBSTANCE: printing antenna having at least one grounded layer with emitting aperture, positioned under which is conductive layer isolated from it by dielectric layer with power field of antenna emitter, which is connected to emitting aperture and made symmetric relatively to its axis and connected to two power lines positioned symmetrically relatively to this axis. Power lines with simultaneous powering of power field in phase and counter-phase allow to realize two antenna polarization directions.
EFFECT: prevented parasitic radiation and ensured possible operation in broad range of frequencies.
2 cl, 12 dwg
FIELD: small-size and high-efficiency antennas for mobile communication devices and handsets.
SUBSTANCE: proposed resonance-tuned multiband microwave antenna radiating in high-frequency band as well as in one or more lower-frequency bands has electricity conducting grounding plane on one surface of insulating substrate, conducting stripline on opposite surface of insulating substrate, and feeder line. Curved slit is made in grounding plane that has feeding end connected due to electromagnetic coupling to feeding end of stripline and loading end connected due to electromagnetic coupling to loading end of stripline. This slit is resonance-tuned and radiates in high-frequency band. Additional electrical conductor connected to grounding plane functions as its extension on loading end and is connected due to electromagnetic coupling to slit in lower-frequency bands so that slit is also resonance-tuned and radiates in lower-frequency band or bands.
EFFECT: reduced size of antenna and impact on its operating characteristics near user's head or body.
44 cl, 54 dwg
FIELD: small-size and high-efficiency antennas for mobile communication devices and handsets.
SUBSTANCE: proposed resonance-tuned multiband microwave antenna radiating in high-frequency band as well as in one or more lower-frequency bands has electricity conducting grounding plane on one surface of insulating substrate, conducting stripline on opposite surface of insulating substrate, and feeder line. Curved slit is made in grounding plane that has feeding end connected due to electromagnetic coupling to feeding end of stripline and loading end connected due to electromagnetic coupling to loading end of stripline. This slit is resonance-tuned and radiates in high-frequency band. Additional electrical conductor connected to grounding plane functions as its extension on loading end and is connected due to electromagnetic coupling to slit in lower-frequency bands so that slit is also resonance-tuned and radiates in lower-frequency band or bands.
EFFECT: reduced size of antenna and impact on its operating characteristics near user's head or body.
44 cl, 54 dwg
FIELD: printing antennas with double polarization with power from commutation field located on electronic board.
SUBSTANCE: printing antenna having at least one grounded layer with emitting aperture, positioned under which is conductive layer isolated from it by dielectric layer with power field of antenna emitter, which is connected to emitting aperture and made symmetric relatively to its axis and connected to two power lines positioned symmetrically relatively to this axis. Power lines with simultaneous powering of power field in phase and counter-phase allow to realize two antenna polarization directions.
EFFECT: prevented parasitic radiation and ensured possible operation in broad range of frequencies.
2 cl, 12 dwg
FIELD: medicine.
SUBSTANCE: emitter of superhigh frequency electromagnetic waves for hyperthermia includes the quarter-wave resonator based on non-symmetrical microstrip transmission line, which consists of dielectric base, screen conductor, emitting conductor and input coaxial plug. The input coaxial plug is installed outside the thermo emission zone of electromagnetic emission from the emitting conductor and radiation field of the source of γ-irradiation, and plugged to the emitting conductor and screen conductor of the microstrip transmission line via L-shaped filter, which includes the strip powering line in power point of the quarter-wave resonator and container.
EFFECT: efficiency of radiation effect on tumor is increased.
2 dwg, 1 tbl
FIELD: radio engineering.
SUBSTANCE: proposed flat cavity antenna, which includes a first low cavity resonator with a partially transparent wall and a second resonant cavity with communication holes, which differs in that the second resonant cavity, is installed inside the first resonant cavity. The first resonant cavity contains the first plate, the first and second volumetric cells, and the second plate, made with emitting holes. The second resonant cavity is made in the form of a coaxial resonator with open ends; slots are made on the outer conductor of the coaxial resonator, the outer and inner coaxial conductors are connected together with a short-circuiting switch. The second resonator is connected with the feeder line.
EFFECT: small sizes of antennas, good antenna matching with the feeder line, low level of lateral and rear emission, low level of cross polarisation emission, high efficiency of the antennas, low losses of electromagnetic energy in the feeder line, low antenna noise temperature, high level of electromagnetic compatibility, aesthetic look.
11 cl, 9 dwg
FIELD: physics; radio.
SUBSTANCE: invention relates to radio engineering, particularly to slotted waveguide antennae, and can be used independently or as a component of a phase antenna array (PAA) with mechanical scanning in two planes or electronic scanning in the E-plane and mechanical scanning in the H-plane. The device consists of a length of waveguide with longitudinal slots made on its wide wall and lying on different sides of axial line. The technical result is achieved due to that, the length of the rectangular waveguide has a flat-topped section with dimensions forming the outer contour on the wide wall a1=(0.45±0.05)λ0 and on the narrow wall b1=(0.26±0.05)λ0 and forming the inner contour with dimensions of the wide wall a2=(0.27±0.05)λ0 and the narrow wall b2=(0.15±0.05)λ0, where λ0 is wavelength in free space. On the wide wall there are metallic edges with radiating slots, where the edges are a continuation of the narrow walls of the outer contour with height equal to λ0/2 or greater, and the length of the radiating slots is greater than λ0/2. Dimensions and displacement relative the axis of the flat-topped waveguide are selected based on the required level of the signal radiated from each slot, and comply with the condition for minimal change of the level of signal radiated from each slot in the given frequency range.
EFFECT: reduced size of the waveguide in the E plane.
2 dwg
FIELD: radio engineering.
SUBSTANCE: planar antenna contains printed symmetrical slot line formed with two identical metal plates which are connected to each other with bonding strip on one side and arranged on one surface of insulating substrate on the other surface of which there located is a piece of signal strip line. Antenna aperture is formed with a piece of divergent printed symmetrical slot line, which is a continued part of the piece of printed homogeneous symmetrical slot line of conductor.
EFFECT: designing broadband antenna capable of simultaneous equal radiation and reception of longitudinal electromagnetic waves and transverse electromagnetic waves with one aperture via separate channels loosened between each other, with low nonuniformity level of matching characteristic, with simple and high-technology construction.
37 cl, 42 dwg
FIELD: radio engineering.
SUBSTANCE: printed-circuit board (50) with control diagram is inserted at least in one spline of contour plate in the device containing contour plate (20) of antenna with multiple antenna splines (30, 31, 32) and at least with one control circuit (40) for excitation of antenna contour plate.
EFFECT: enlarging functional capabilities and improving compactness.
15 cl, 4 dwg

FIELD: radio engineering, communication.
SUBSTANCE: circular polarisation slit stripline leaky-wave antenna includes a dielectric substrate, on the lower metal-coated side of which there is a spiral-shaped microstrip feed line, and on the top metal-coated side of which there are main slit radiators twisted on a spiral around the geometric centre of the antenna and having straight and curved segments of different length; on the top metal-coated side of the dielectric substrate between the main slit radiators there are additional slits with a shorter electrical length than that of the main slit radiators; the additional slits are not connected to the main slit radiators and are in form of concentric arcs arranged around the geometric centre of the antenna or in form of spiral sections.
EFFECT: improved technical characteristics of the antenna, specifically: low elliptic coefficient, improved suppression of cross-polarisation and wider operating frequency range.
2 cl, 11 dwg
Slot Antenna Resonant Frequency
FIELD: radio engineering, communication.
SUBSTANCE: waveguide line, on one wall of which there are radiating elements and at the end of which there is a tuning element, includes phase-shifting devices mounted between radiating elements and between a radiating element and the tuning element, and communication elements connected to the waveguide, wherein the phase-shifting devices change the phase of the transmitted microwave signal in a wide range depending on its power level.
EFFECT: wide operating frequency range without deterioration of the directivity index and matching the antenna while maintaining the direction of the main directional lobe, as well as low cost and high technological effectiveness.
1 dwg
FIELD: radio engineering, communication.
SUBSTANCE: aircraft antenna comprises a cylindrical resonator open at one end, which is partially filled with a dielectric, a matching element, a coaxial connector, a tuning element, a radiator and a top cover. The centre conductor of the coaxial connector is extended into the inside of the cylindrical resonator and is connected to the radiator. The matching element is in form of two stub lines. The first stub line is placed parallel to the centre conductor of the coaxial connector. The second stub line is connected by one end to the side wall of the cylindrical resonator and by the other end to a portion of the radiator located between the points of connection with the centre conductor and the first stub line. The radiator is in form of a ring and is rigidly mounted on the dielectric. The radiator is mounted such that the axes of symmetry of the radiator and the cylindrical resonator and the straight line passing through the middle of said portion of the radiator parallel to the axis of symmetry of the radiator lie in one plane of the longitudinal section of the antenna. The tuning element is mounted in the bottom cover of the cylindrical resonator under the radiator while allowing axial displacement thereof.
EFFECT: simple design of the radiator, smaller dimensions, improved manufacturability, broader functional capabilities, high reliability.
6 dwg
There Ain’t No Free Lunch
OK. The English is bad but the title says it all. So many hams are looking for that “all band, does everything” HF antenna.
On VHF and UHF the “tuning” of an antenna is far less critical than on HF. The wavelengths at 144 MHz and above provide a naturally wide bandwidth so that you assemble the antenna and, in most cases, it just works. Nearly all transmitting antennas at VHF and above are resonant types.
There are basically only two classes of HF antennas: Resonant and Non-Resonant. Let’s look at resonant antennas first.
Resonant antennas include (but are not limited to) monoband dipoles, monoband and trapped verticals, mono-band and trapped multiband Yagis, and specialized multiband antennas like fan and parallel dipoles. Resonance may be designed into these antennas by the use of traps, linear loading, stubs, or by the natural resonance of the length of the radiator. With these antennas, resonance occurs only in narrow chunks of spectrum.

Non-resonant antennas include (but are not limited to) long-wires, un-trapped multiband verticals, off-center fed dipoles, and other compromise antennas. These antennas typically require a wide-range antenna tuning unit (ATU).
On HF, the wavelengths are long to very long and resonance becomes more critical. A dipole on 80 meters may have a useful SWR bandwidth of only 60 kHz or so. If you want to work 75 phone with an 80 meter CW antenna, you’ll need an ATU (better referred to as a transmatch) to compensate. All resonant HF antennas – ALL OF THEM – used outside their resonant bandwidth require the use of a tuner. If you are looking for an antenna that will cover 160 through 6 and work efficiently… that hasn’t been invented yet.
Non-resonant antennas may be force-fed using ATUs in conjunction with baluns or feedline current chokes. Baluns and chokes will keep RFI out of your shack and allow the tuner to force-feed the non-resonant antenna so that power is radiated instead of being lost in standing waves or impedance losses. For example, 43 foot verticals are 43 feet long to avoid accidental resonance. In other words, they’re designed to be totally non-resonant. Their balun or unun and associated ATU allow them to work across a very wide spectrum. The lower the frequency, however, the poorer the efficiency of these antennas becomes.
Compromise antennas require compromise solutions and support. There ain’t no free lunch!